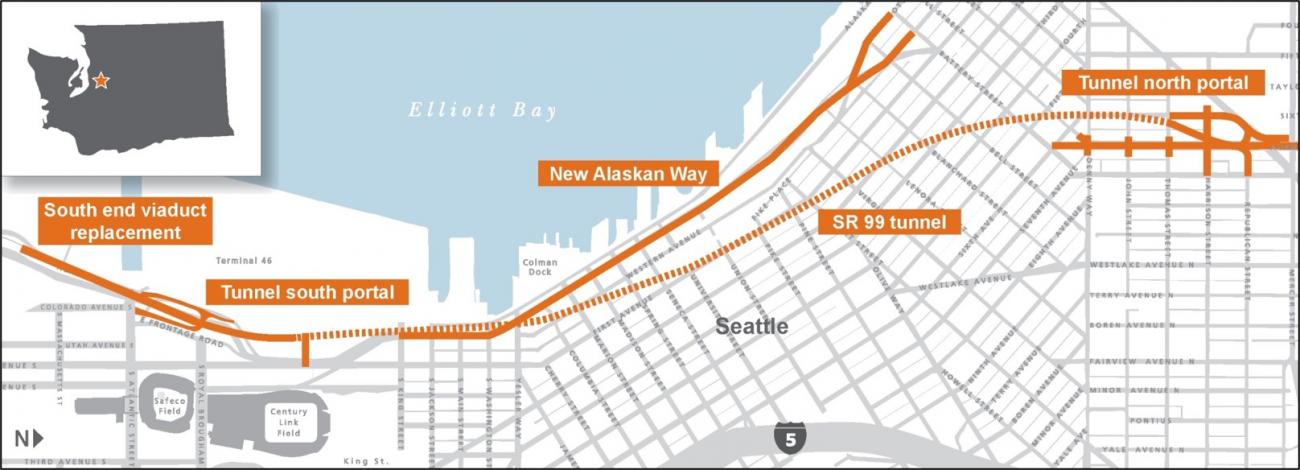
The Alaskan Way Viaduct Replacement Program consisted of more than 30 projects that transformed the SR 99 corridor through downtown Seattle and along Seattle's central waterfront. Key accomplishments include:
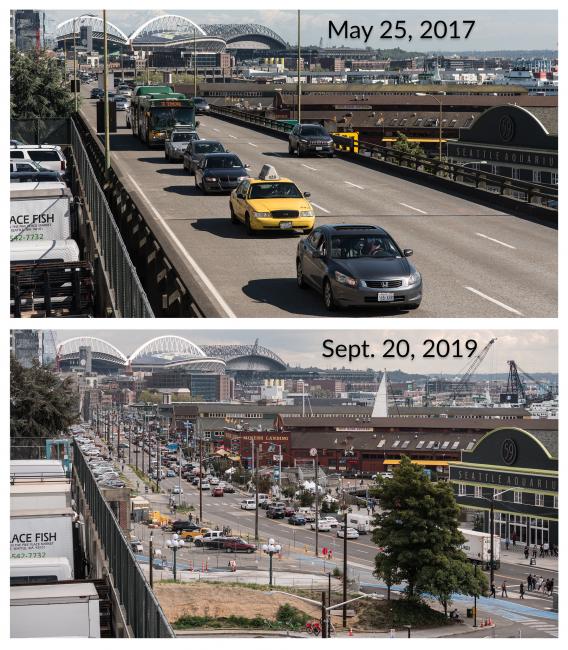
- Demolition of the Alaskan Way Viaduct between South Holgate and Bell streets and the decommissioning of the Battery Street Tunnel. Removing the viaduct made it possible for the city of Seattle to build the new Alaskan Way and Waterfront Park along the waterfront.
- Completion of the SR 99 tunnel under downtown Seattle.
- Street improvements around the tunnel’s south portal near Seattle’s stadiums and the tunnel’s north portal in Seattle’s South Lake Union neighborhood.
The Alaskan Way Viaduct, an elevated section of State Route 99 in Seattle, was built in the 1950s and 1960s, and decades of daily wear and tear took a toll on the structure. The structure was weakened in the 2001 Nisqually earthquake, requiring emergency repairs. Because of the viaduct’s age and vulnerability to earthquakes, replacing it was critical to public safety.
The state's viaduct replacement projects, including the SR 99 tunnel, are estimated to cost $3.35 billion. Funding came from state, federal and local sources, as well as the Port of Seattle and tolls.
This section intentionally omitted.
Completed projects
The SR 99 Tunnel: A two-mile-long tunnel beneath downtown Seattle.
Battery Street Tunnel and North Surface Streets: Decommissioning the Battery Street Tunnel and rebuilding three blocks of Seventh Avenue North in South Lake Union.
Viaduct Demolition: This project removed the Alaskan Way Viaduct along Seattle's central waterfront after the SR 99 tunnel opened. Full demolition began in February 2019 and the final segment of the viaduct was removed in November 2019. This work was part of the Battery Street Tunnel and North Surface Streets project contract.
Holgate to King Street: This project built a mile-long stretch of new SR 99 highway near Seattle’s stadiums, replacing the Alaskan Way Viaduct's southern mile. The project also built an overpass near South Atlantic Street that allows traffic to bypass train blockages near Seattle’s busiest port terminal. The project ran from 2011 to 2014, with a budget of $347.7 million.
South Access - Surface Street Connections: Completing surface street connections around the SR 99 tunnel's south portal by Seattle's stadiums.
New Alaskan Way: A new Alaskan Way surface street along Seattle's central waterfront that provides multimodal connections between SR 99 and downtown.
View program photos on WSDOT's Flickr page.
View AWV videos on WSDOT's YouTube channel.
The view of Seattle's central waterfront before and after the SR 99 tunnel opened and the Alaskan Way Viaduct was demolished.
![]()